All Categories
Featured
Two people acquisition joint annuities, which offer a surefire revenue stream for the remainder of their lives. If an annuitant passes away throughout the distribution period, the continuing to be funds in the annuity might be passed on to a designated recipient. The certain alternatives and tax obligation implications will depend on the annuity agreement terms and relevant regulations. When an annuitant dies, the passion earned on the annuity is dealt with in a different way depending upon the sort of annuity. With a fixed-period or joint-survivor annuity, the interest continues to be paid out to the surviving beneficiaries. A survivor benefit is an attribute that makes certain a payment to the annuitant's recipient if they pass away before the annuity settlements are worn down. The schedule and terms of the fatality advantage might vary depending on the certain annuity agreement. A type of annuity that quits all settlements upon the annuitant's fatality is a life-only annuity. Recognizing the terms of the fatality advantage before buying a variable annuity. Annuities go through taxes upon the annuitant's fatality. The tax obligation treatment relies on whether the annuity is held in a qualified or non-qualified account. The funds are subject to revenue tax obligation in a qualified account, such as a 401(k )or individual retirement account. Inheritance of a nonqualified annuity usually leads to tax just on the gains, not the whole amount.
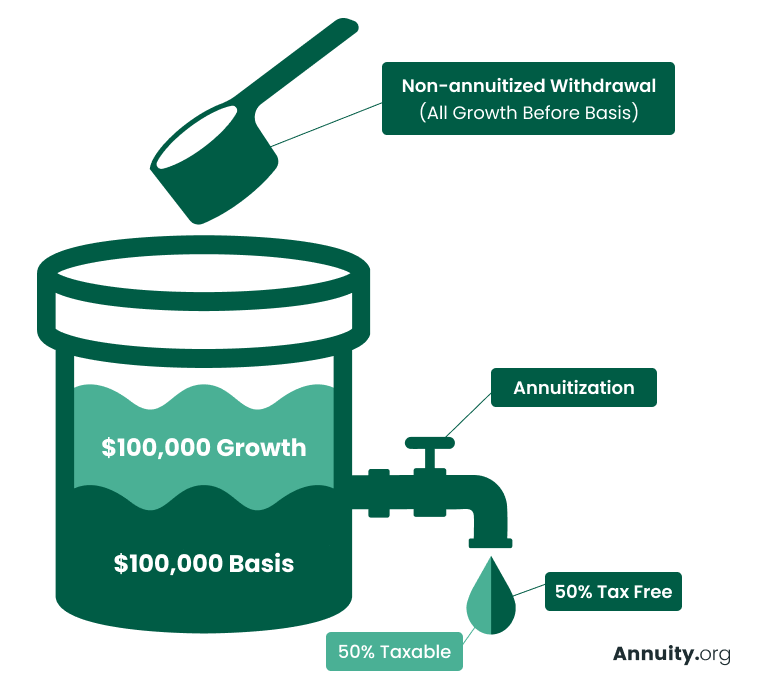
The initial principal(the quantity initially deposited by the parents )has already been taxed, so it's exempt to tax obligations again upon inheritance. Nevertheless, the profits section of the annuity the rate of interest or financial investment gains accrued in time undergoes income tax. Normally, non-qualified annuities do.
have died, the annuity's advantages usually return to the annuity proprietor's estate. An annuity proprietor is not legitimately called for to notify existing beneficiaries regarding modifications to recipient designations. The decision to alter recipients is commonly at the annuity proprietor's discretion and can be made without alerting the present recipients. Since an estate practically does not exist till an individual has passed away, this beneficiary classification would just come into result upon the fatality of the named person. Typically, when an annuity's owner passes away, the assigned recipient at the time of fatality is qualified to the benefits. The partner can not alter the recipient after the owner's death, even if the beneficiary is a small. However, there might specify provisions for managing the funds for a small beneficiary. This frequently includes appointing a guardian or trustee to take care of the funds until the kid maturates. Usually, no, as the recipients are exempt for your debts. It is best to seek advice from a tax professional for a particular answer related to your instance. You will remain to obtain settlements according to the contract routine, but attempting to get a swelling amount or financing is likely not a choice. Yes, in mostly all cases, annuities can be inherited. The exception is if an annuity is structured with a life-only payment alternative through annuitization. This kind of payout discontinues upon the death of the annuitant and does not give any kind of residual value to beneficiaries. Yes, life insurance policy annuities are typically taxable
When taken out, the annuity's incomes are strained as common income. The primary amount (the initial investment)is not exhausted. If a beneficiary is not named for annuity benefits, the annuity proceeds generally go to the annuitant's estate. The distribution will adhere to the probate process, which can postpone settlements and might have tax obligation ramifications. Yes, you can name a depend on as the recipient of an annuity.
Tax implications of inheriting a Fixed Annuities

Whatever part of the annuity's principal was not already strained and any type of earnings the annuity gathered are taxable as earnings for the beneficiary. If you inherit a non-qualified annuity, you will just owe tax obligations on the earnings of the annuity, not the principal utilized to purchase it. Since you're getting the entire annuity at once, you must pay taxes on the whole annuity in that tax obligation year.
Latest Posts
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options A Closer Look at How Retirement Planning Works Breaking Down the Basics of Deferred Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Ret
Breaking Down Your Investment Choices A Comprehensive Guide to Annuity Fixed Vs Variable Defining What Is Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Choosing t
Understanding Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity Everything You Need to Know About Financial Strategies What Is Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity? Benefits of Choosing
More
Latest Posts